
By Dr. Priya Shikha Modi, MBBS, MS, DNB (gynecology and obstetrics), FMAS (Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery) What is abnormal...
MODILIFELINE – Best gynecologist in noida
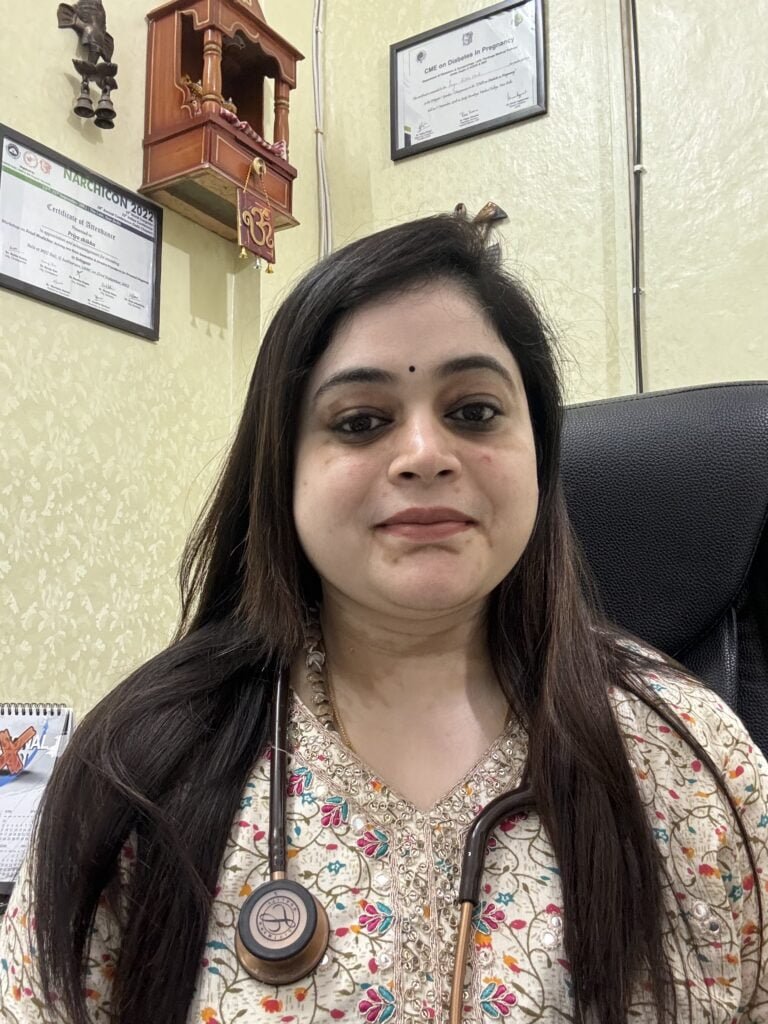
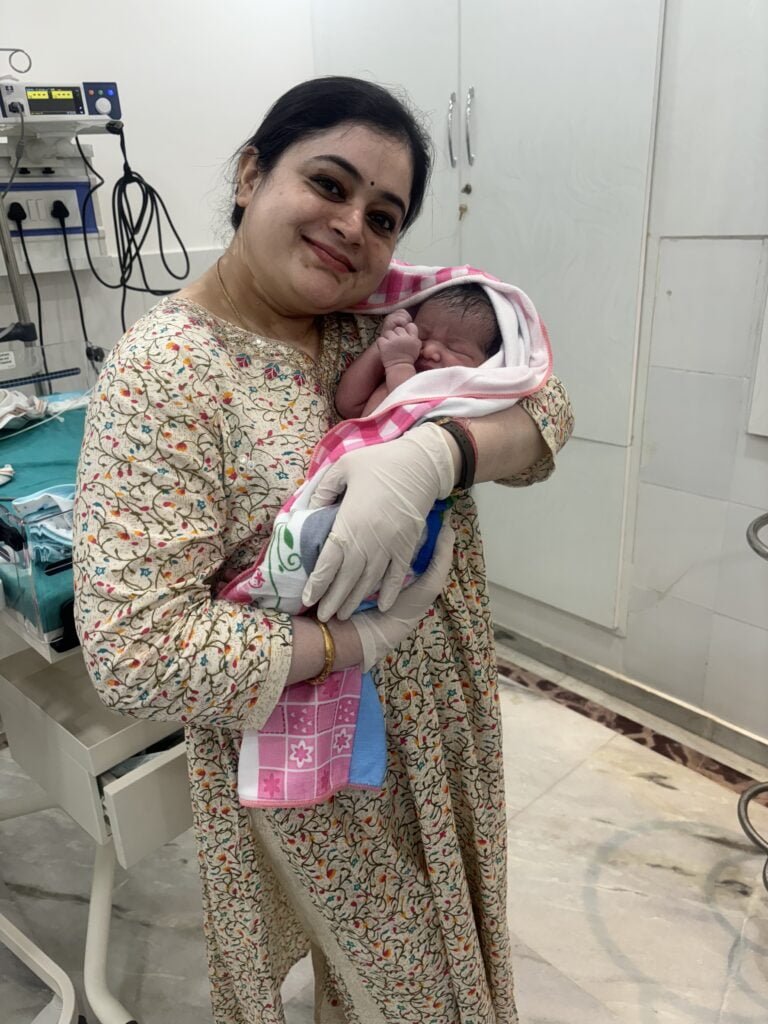





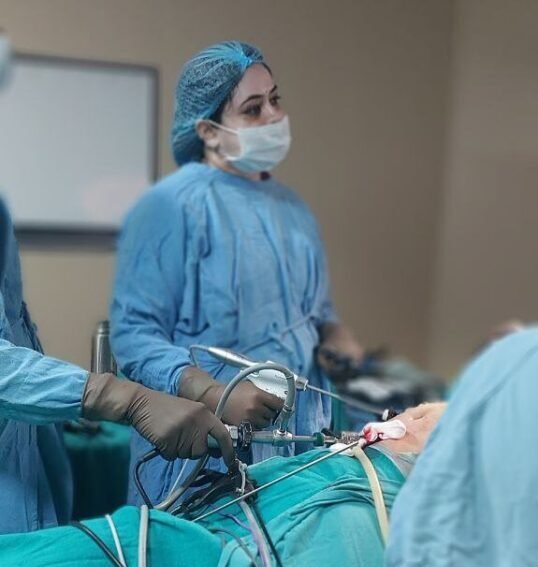
Dr. Priya Shikha Modi is a highly accomplished obstetrician, infertility specialist and gynecologist in Noida sector 53, India. She has a strong background in gynecology and laparoscopic surgery, having achieved top ranks in the national entrance examination and completing her MBBS degree from Sarojini Naidu Medical College, Agra. She also holds a master’s in surgery from the University College of Medical Sciences (UCMS) in Delhi. Dr. Priya Shikha Modi worked as a senior doctor at Guru Teg Bahadur Hospital for three years and excelled in fellowship training in minimal access surgery at the World Laparoscopy Hospital in Gurgaon. Her dedication to women’s health has earned her a reputation as one of the best gynecologists in the country. Her extensive training and compassionate approach allow her to provide exceptional care for her patients. Her contributions to women’s health are remarkable, and her expertise in gynecology and laparoscopic surgery ensures the highest quality care tailored to individual needs.
Obstetrician-gynecologist is the depart of a woman's care of reproductive organs and health. Obstetrics involves the treatment of pregnant women, including the delivery of babies.
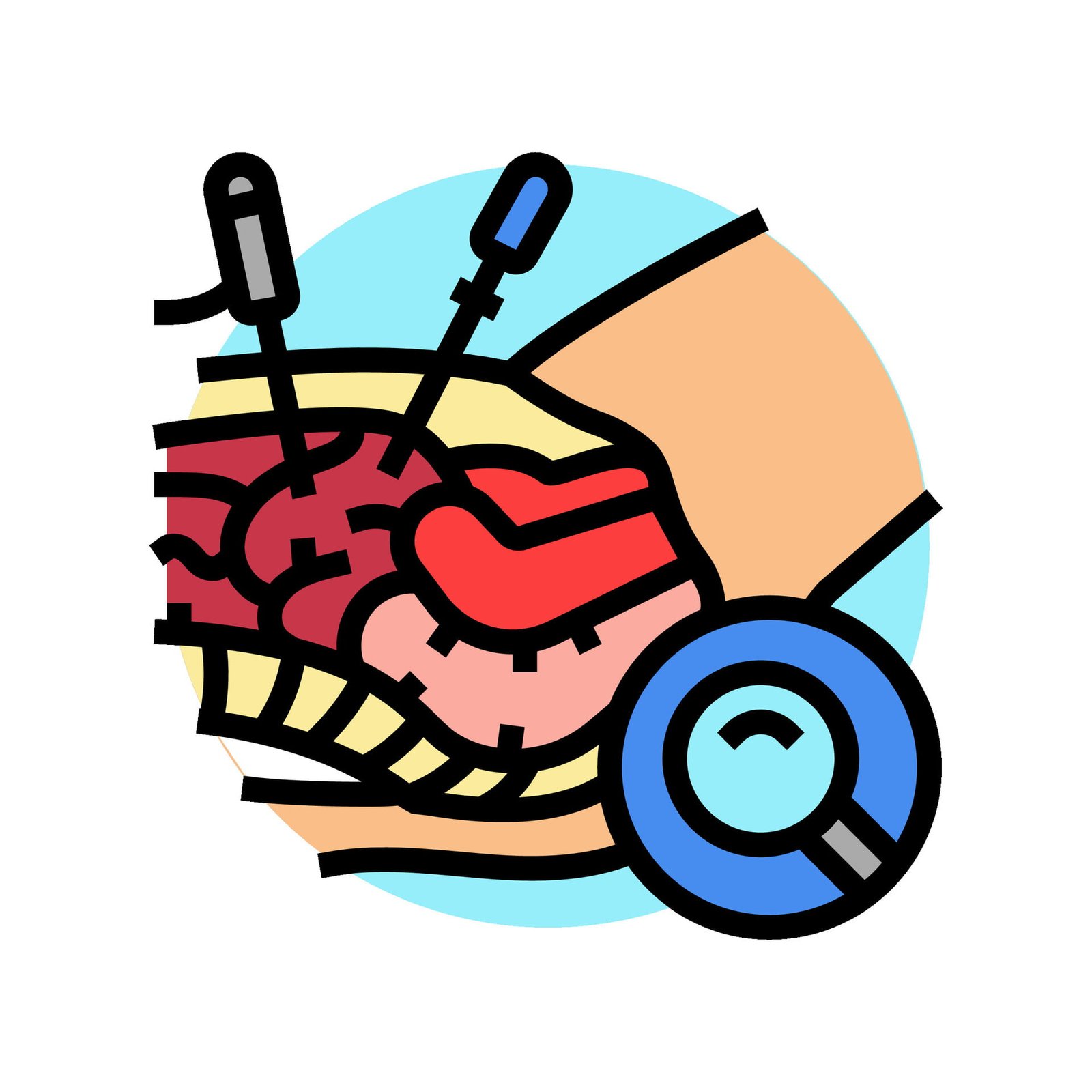

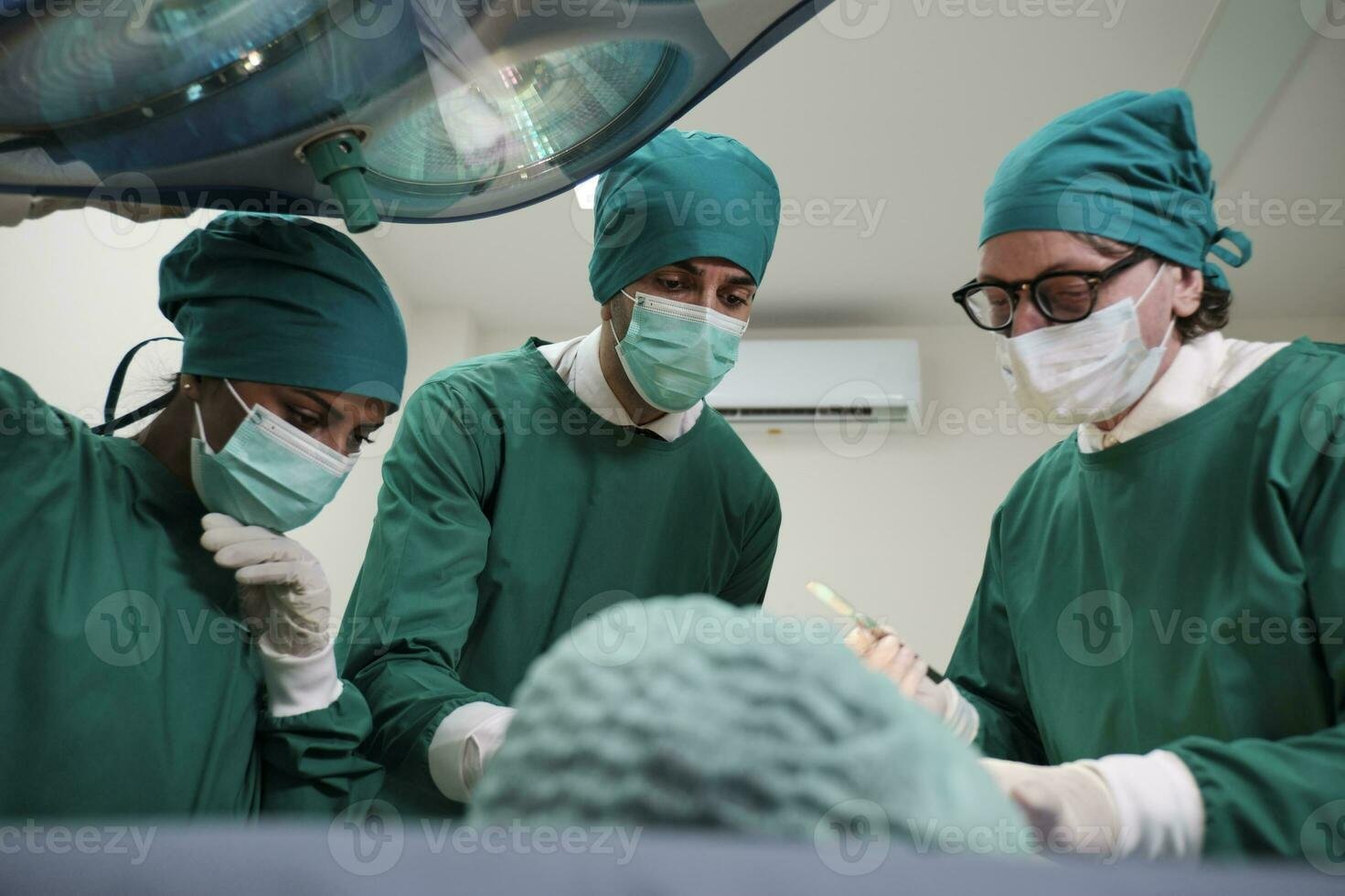
Gynaecological laparoscopy is a procedure to examine the pelvis, womb, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, aiding in diagnosis and treatment. It's a safer alternative to open surgery, with fewer complications and shorter recovery time.
Family planning involves various contraceptives, surgical procedures, and barrier methods to help individuals decide when and if to have children.

Infertility, a condition where one year of pregnancy is unsuccessful, can be caused by ovulatory disorders, endometriosis, low sperm count, or low testosterone, with age-related risk increasing.
Puberty concerns include delayed, precocious, contrasexual pubertal development, premature adrenarche, premature thelarche in girls, and premature or delayed menarche.
We provide state-of-the-art pregnancy & childbirth care for the vast majority of the women
Menopause, a natural biological process, occurs after 12 months without a menstrual cycle, typically occurring in the 40s or 50s. Symptoms include hot flashes and emotional distress, but treatments include lifestyle adjustments and hormone therapy

Cosmetic Gynecology is a sub-specialty combining plastic surgery and gynecology, focusing on cosmetic procedures to enhance the appearance and function of the outer and inner vagina.

Gynecologic oncologists provide comprehensive diagnosis and surgical management of various cancerous and benign conditions in the female reproductive system, including cervical, endometriosis, fibroids, ovarian, pelvic, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar cancer

Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition where ovaries produce abnormal amounts of androgens, male sex hormones, causing cysts in the ovaries. Ovulation occurs when a mature egg is released, fertilized by male sperm, or sent out during menstruation.
Modilifeline Women’s Clinic Redefining Women’s Health.
MBBS, MS, DNB (gynecology and obstetrics), FMAS (Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery), laparoscopic surgeon, Infertility Specialist



We have a clinic that offers a positive environment, with the best gynecologist and gynecological laparoscopic surgeon in the country and a trained nurse with 11 years of experience. Our clinic is easy to reach by metro (Near metro station sector 34 Noida)
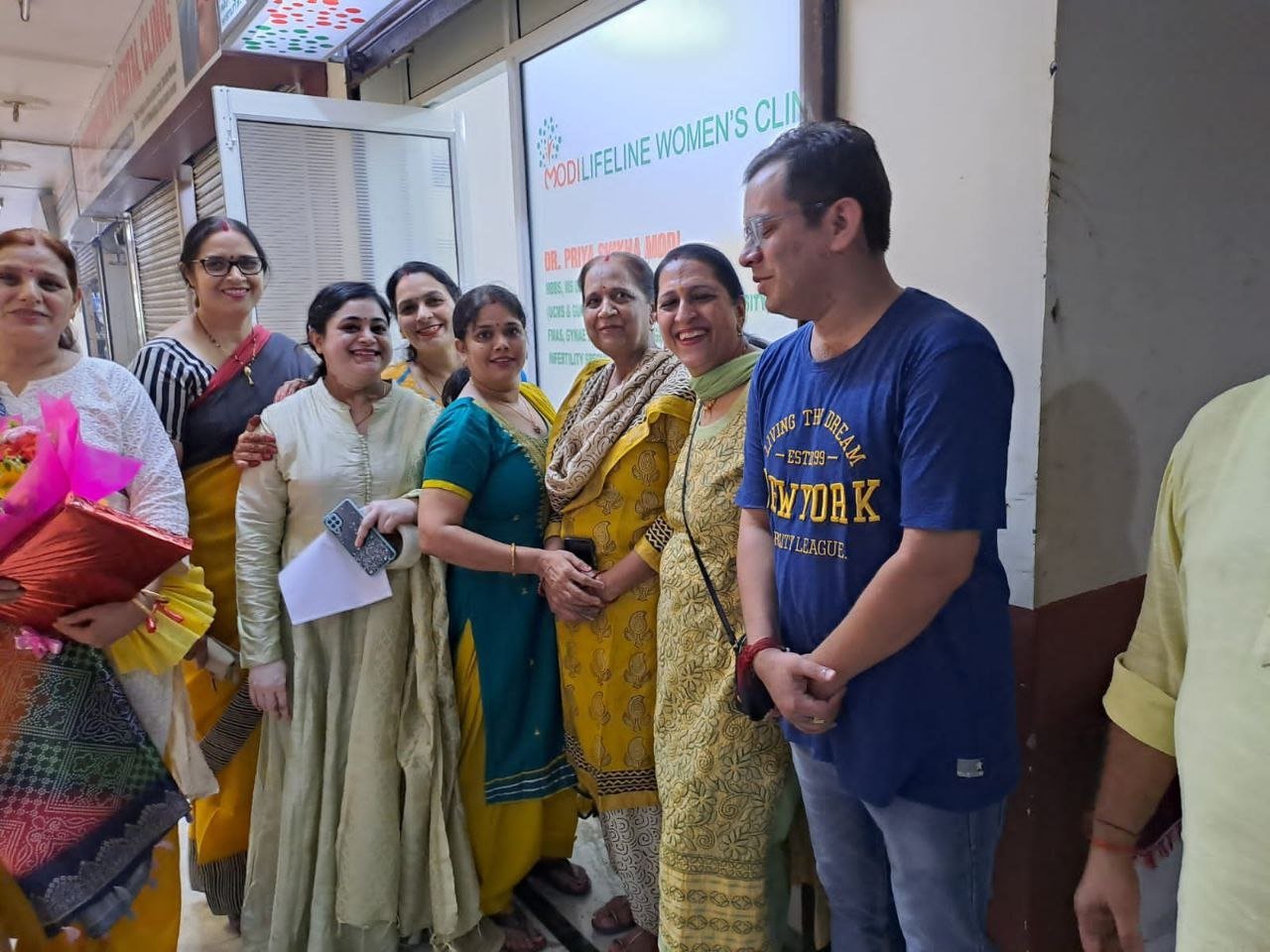
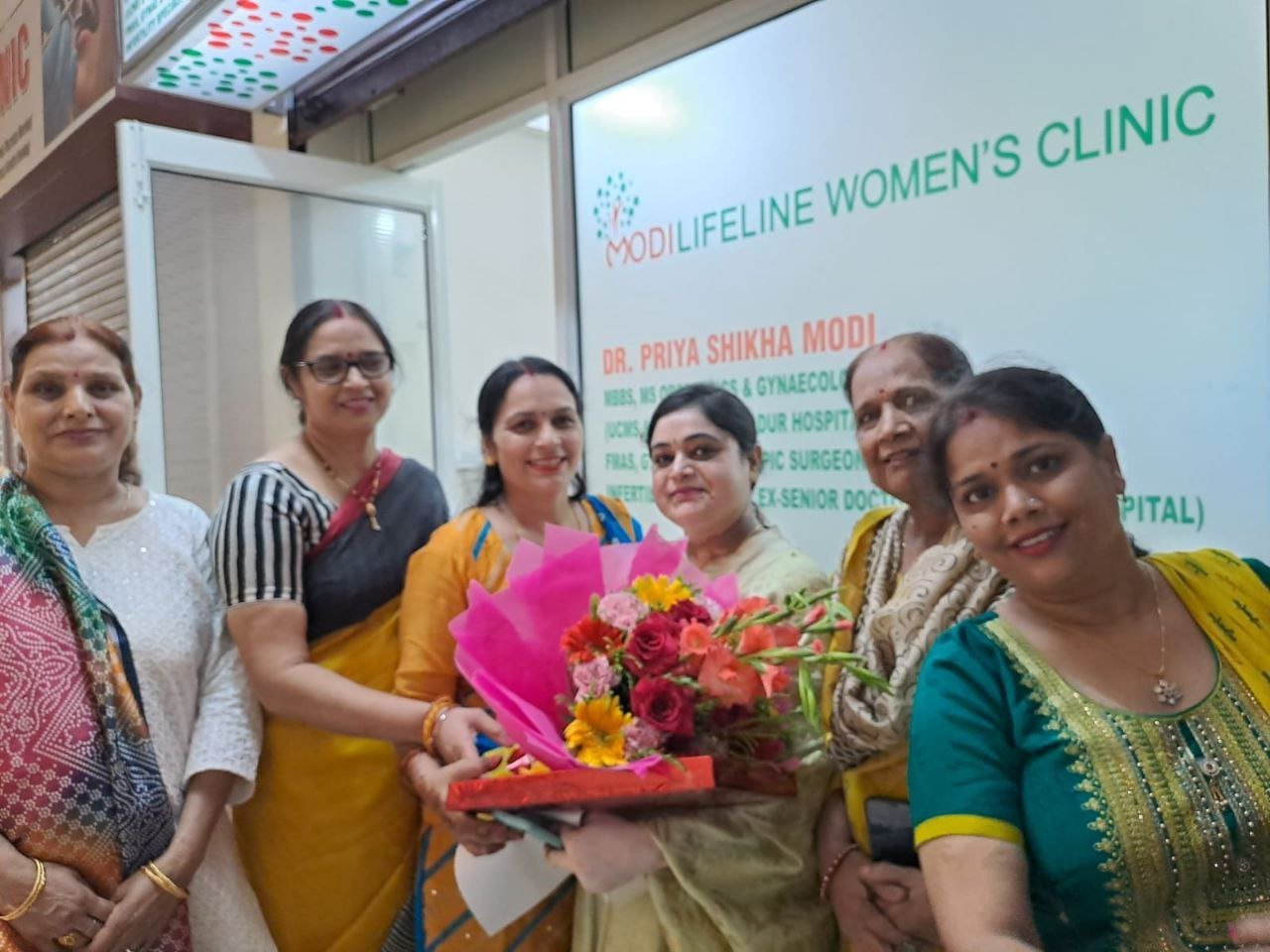
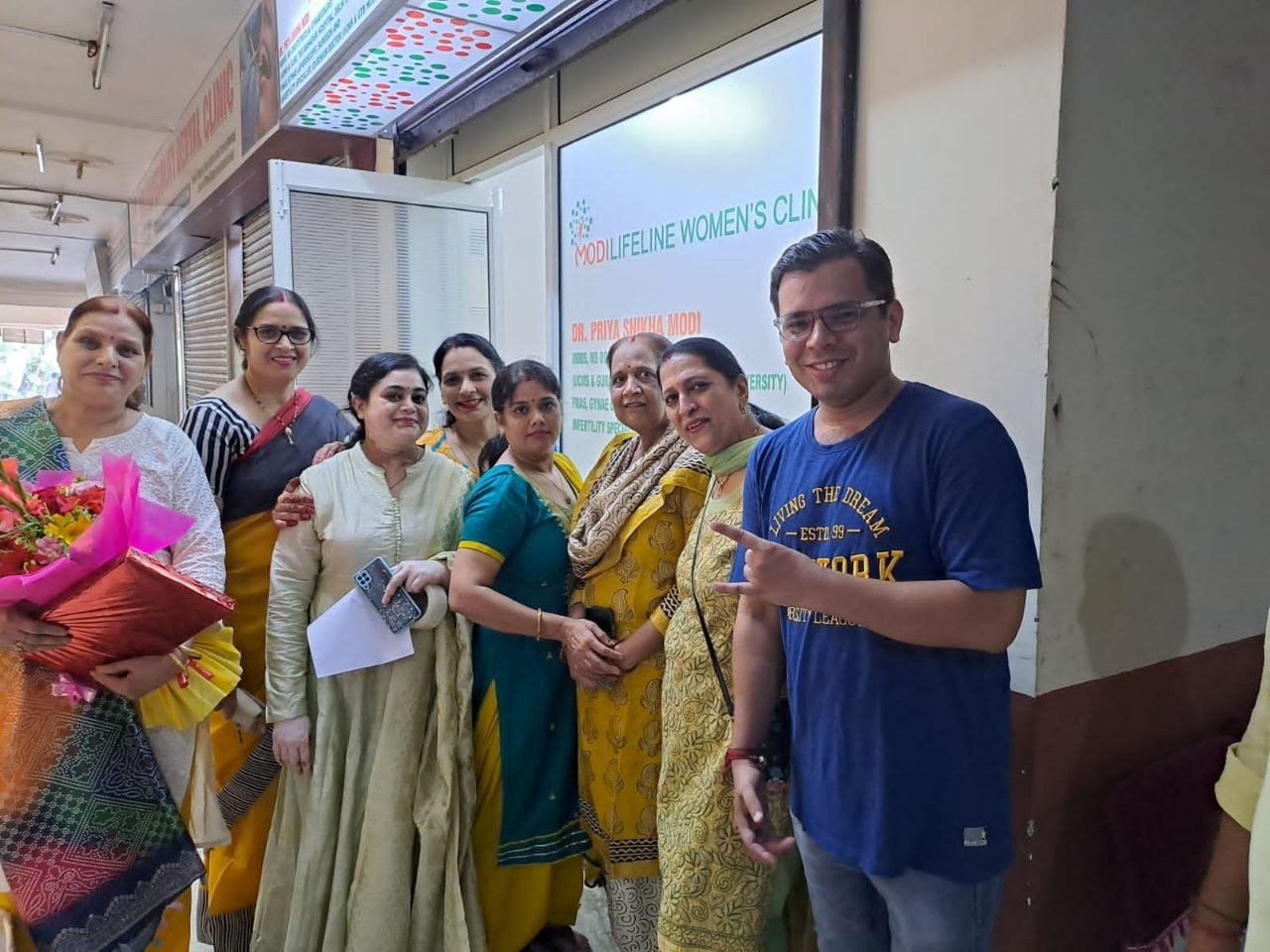
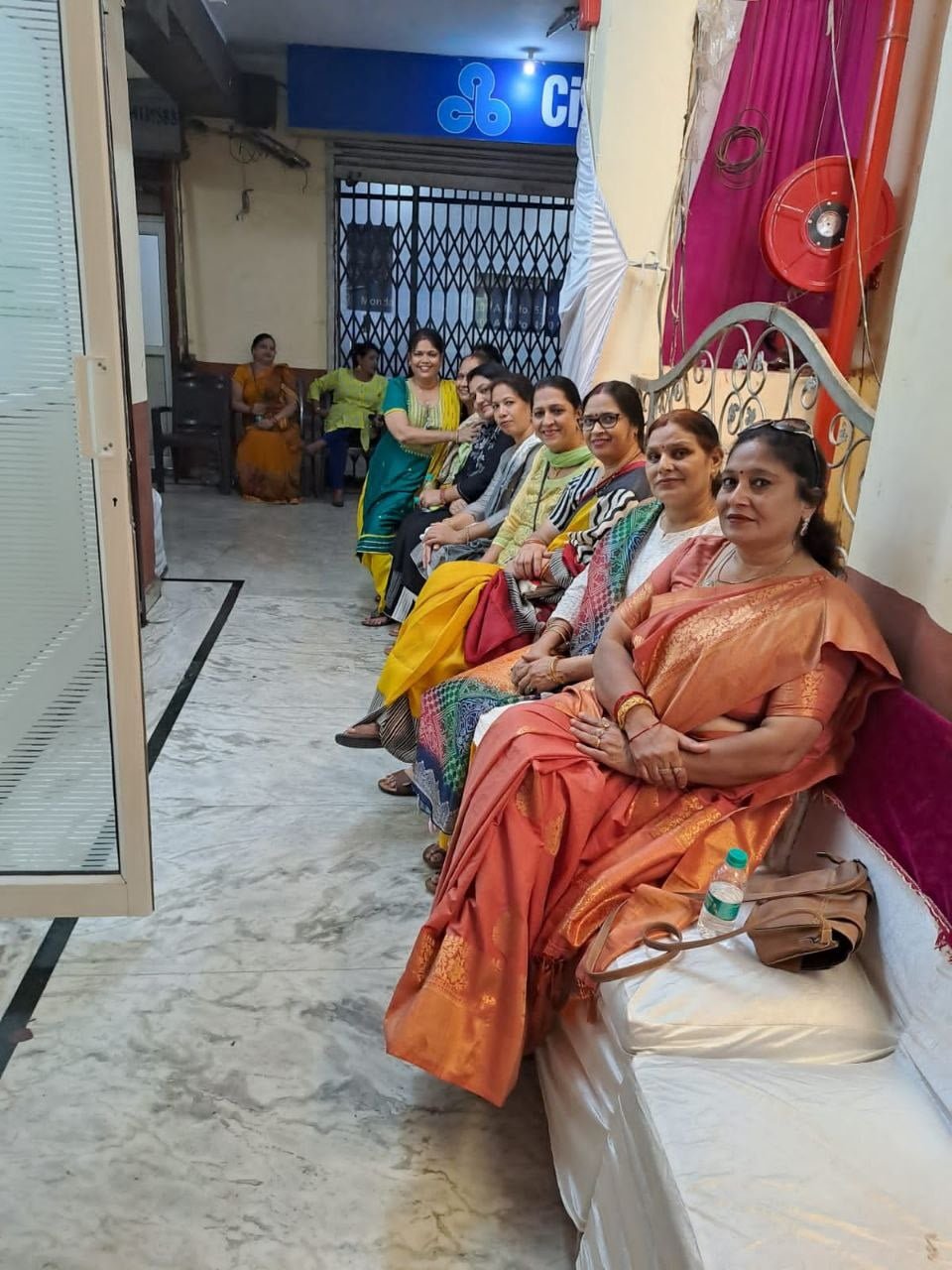
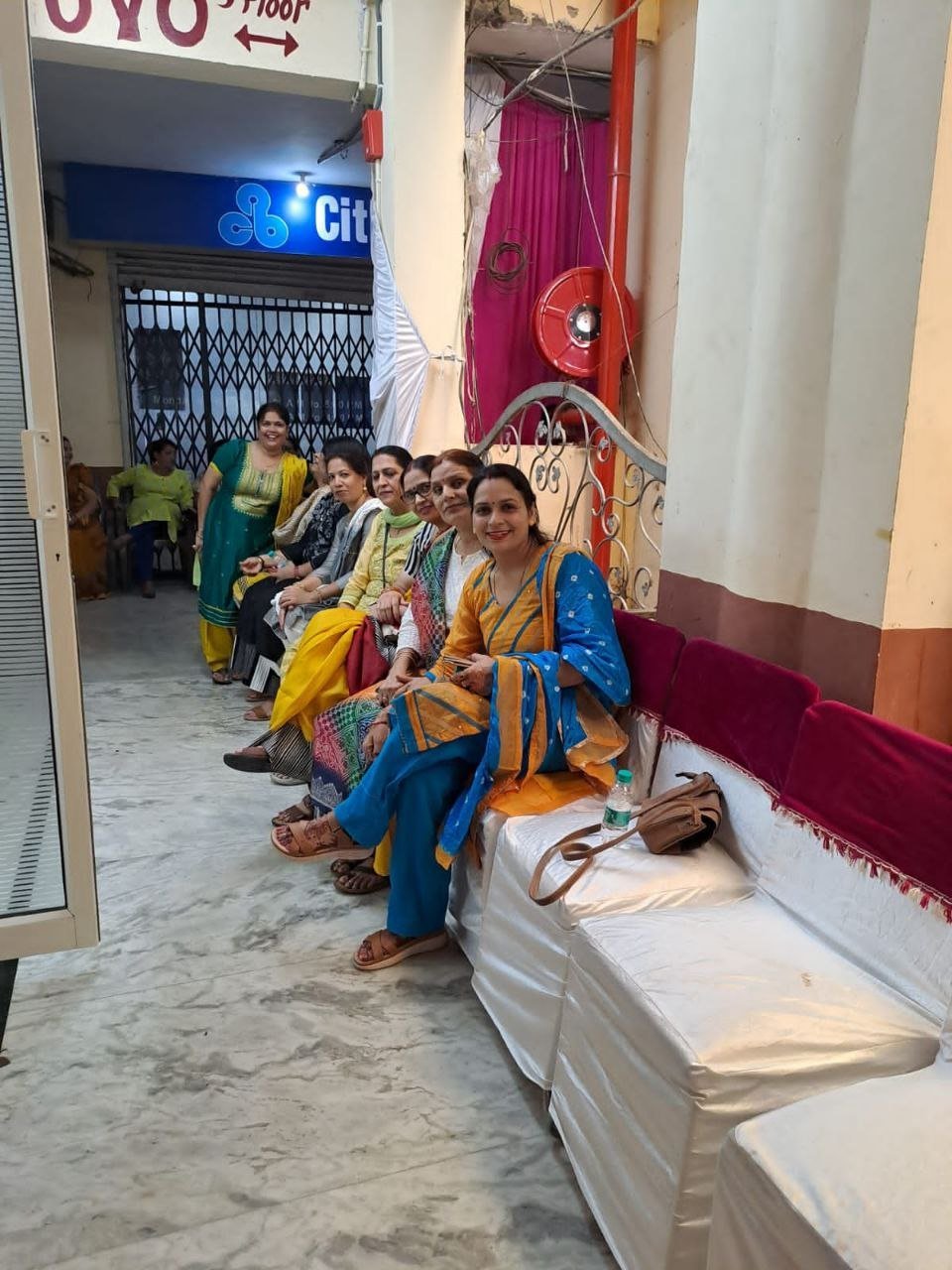
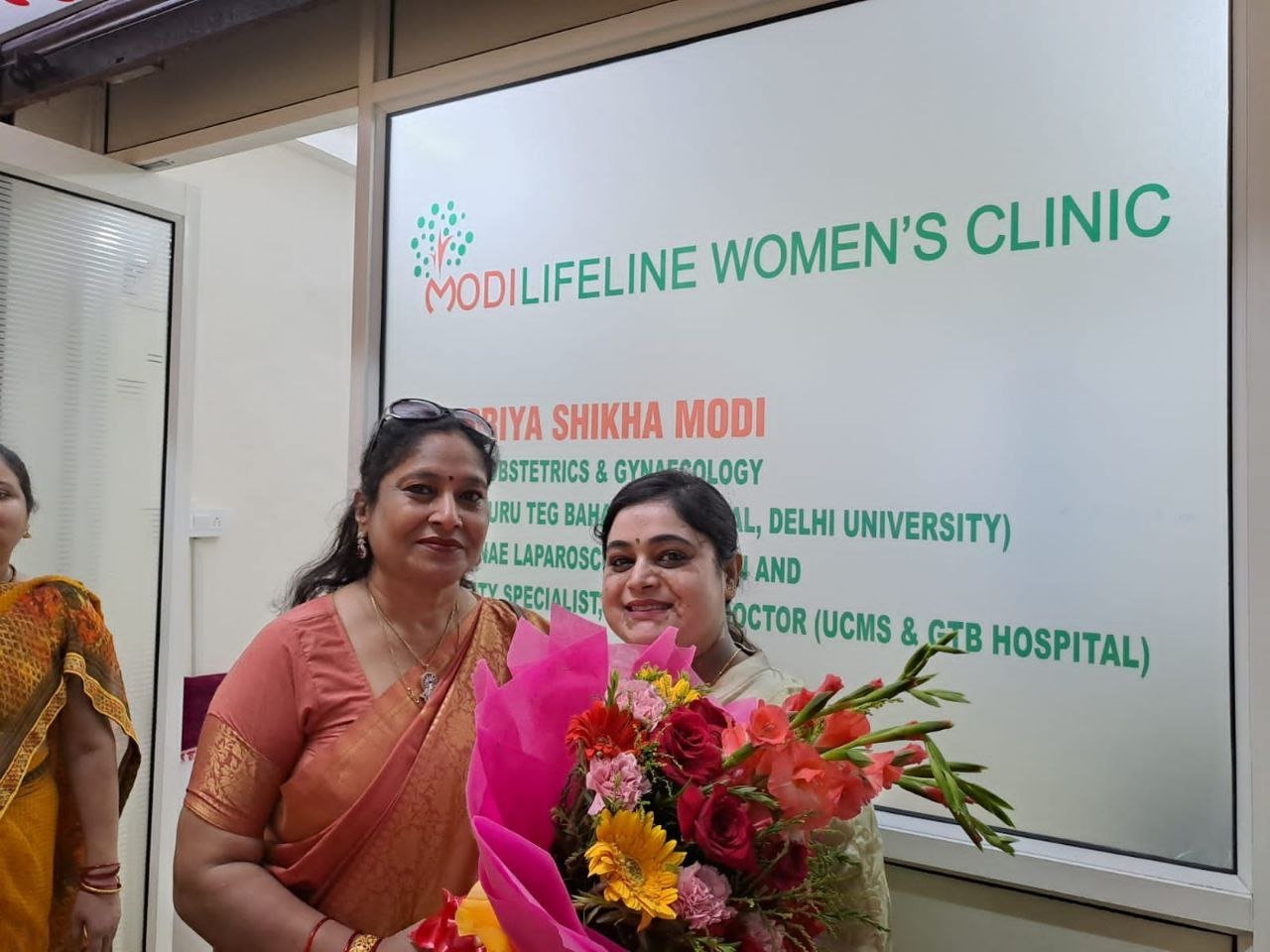
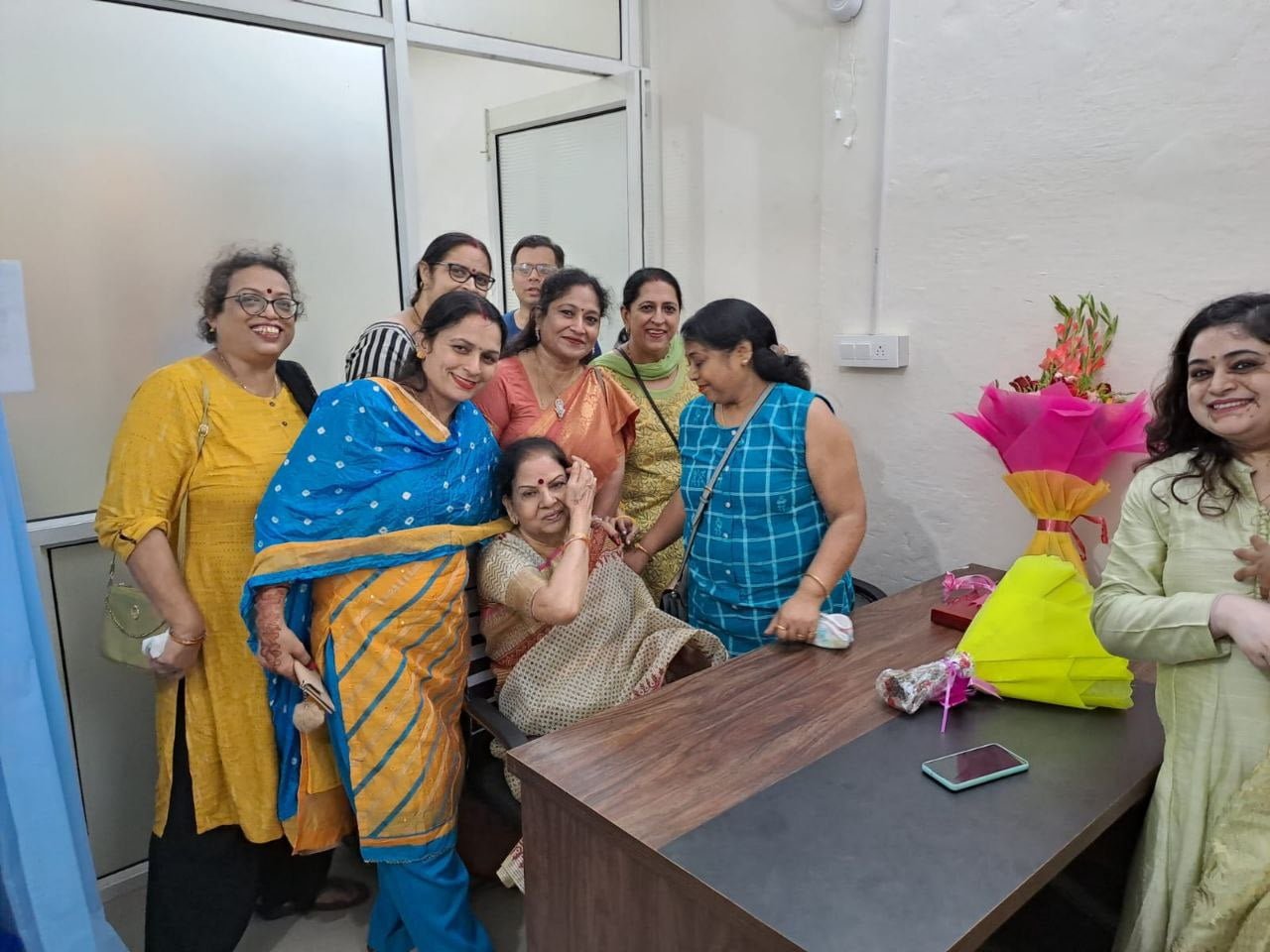
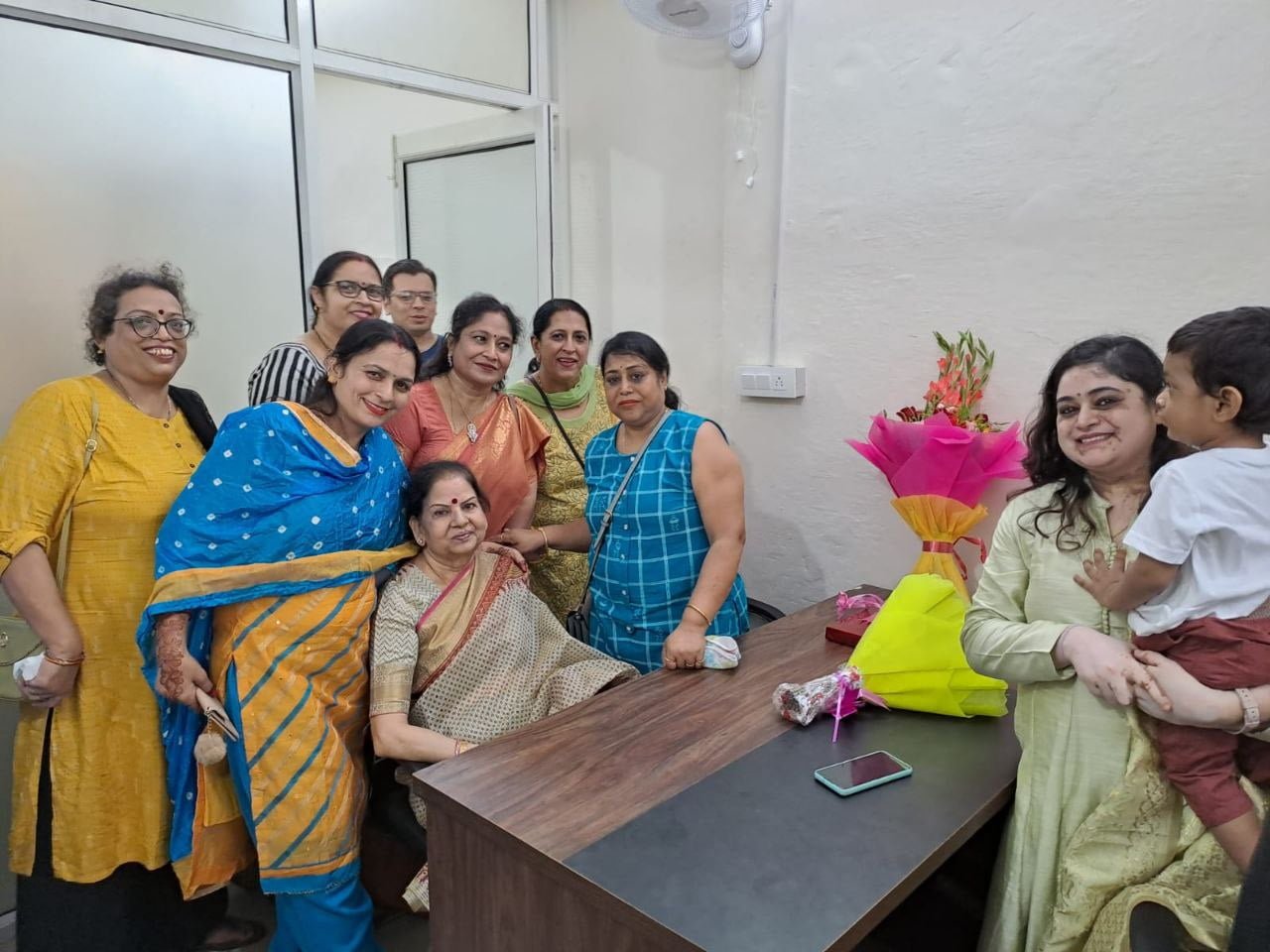
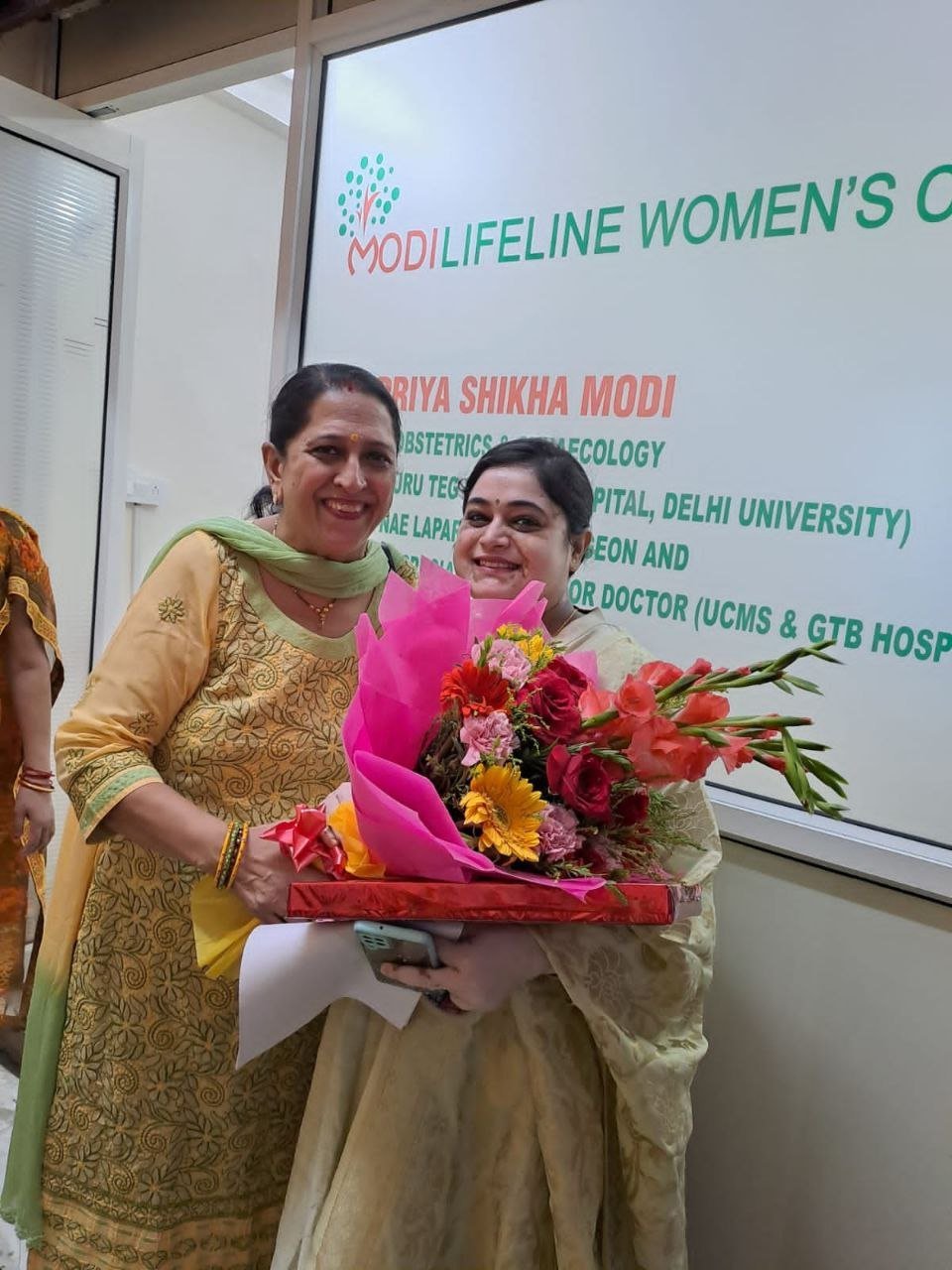

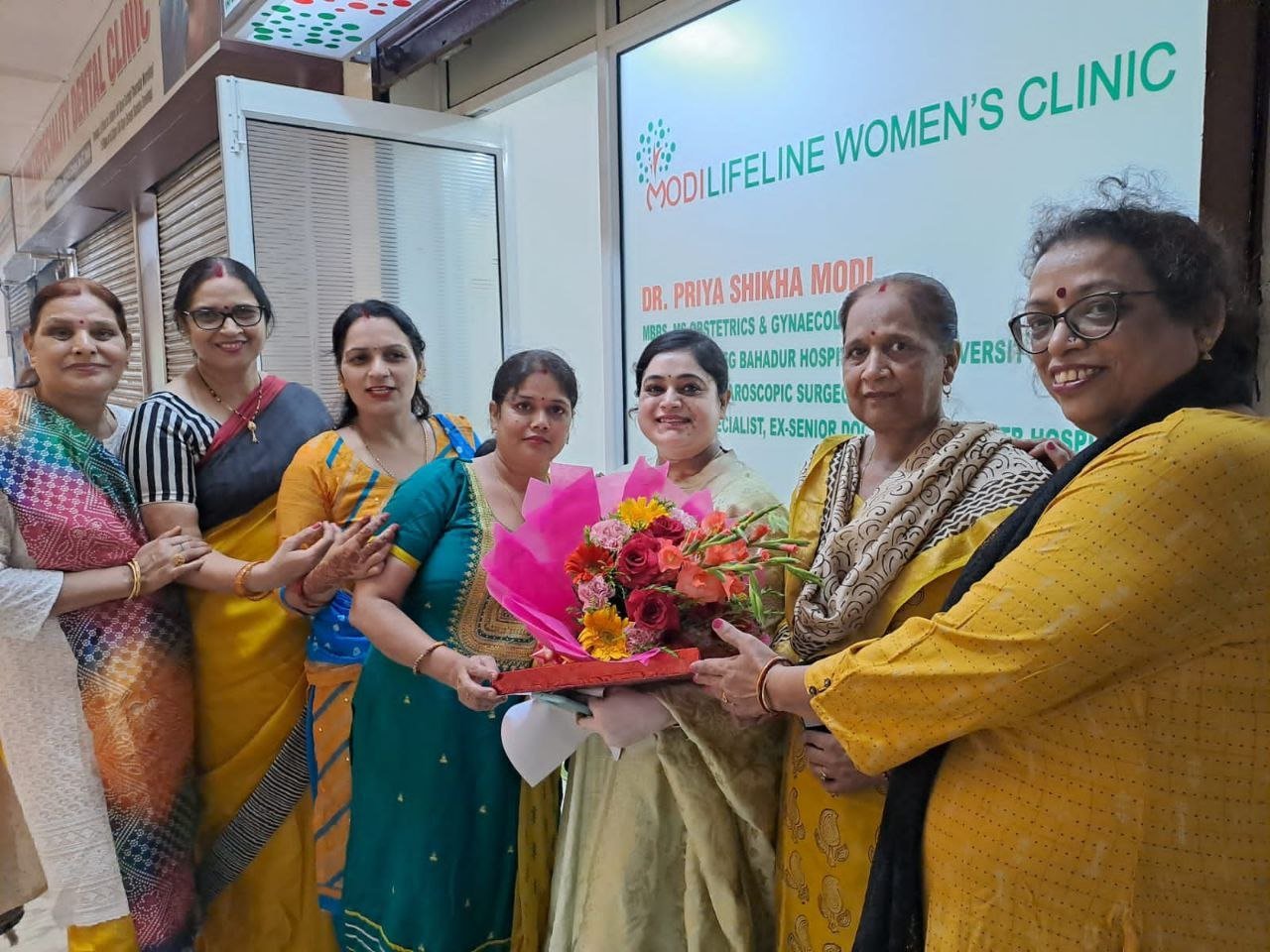








On September 15, 2022, two prominent leaders inaugurated the Modilifeline women’s clinic in Sector 53 Noida, a new facility that aims to redefine women’s health. The chief guests were Vimla Batham, the President of the U.P. State Commission for Women and former MLA of Noida, and Nawab Singh Nagar, the former State Minister of the UP Government and former Vice President of the BJP Uttar Pradesh, who also served as an MLA of Noida.
Both Vimla Batham and Nawab Singh Nagar praised the initiative and expressed their hope that the clinic would serve as a model for women’s health in the country. They also appreciated the efforts of Dr. Priya Shikha Modi, the founder and director of Modilifeline women’s clinic, who has over nine years of experience in women’s health. Dr. Modi thanked the guests and attendees for their support, saying that her vision was to create a safe and comfortable space for women to access the best health care possible.
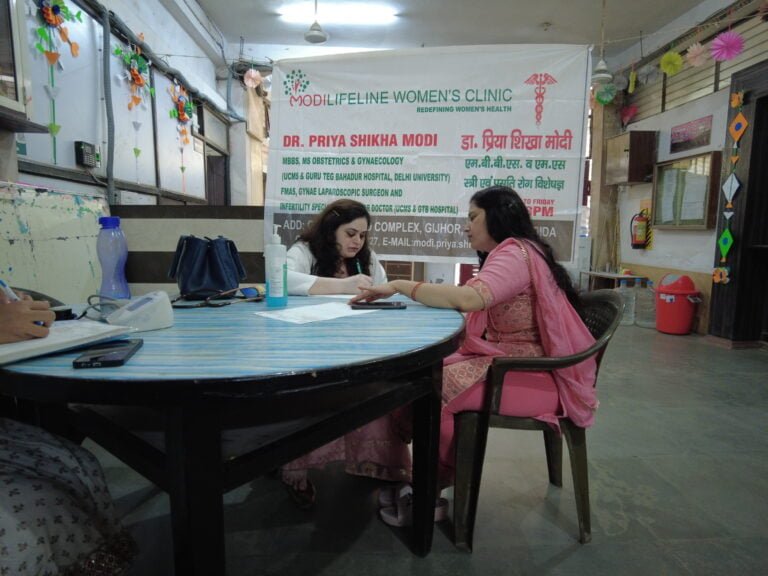
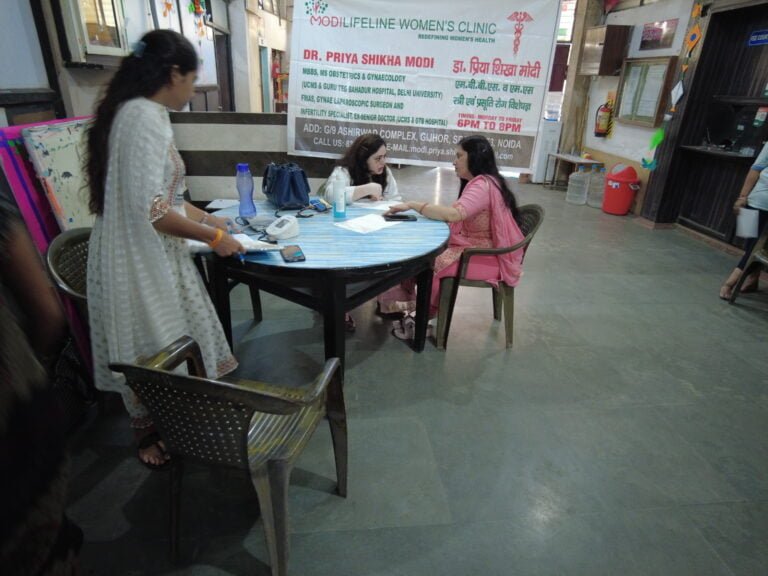
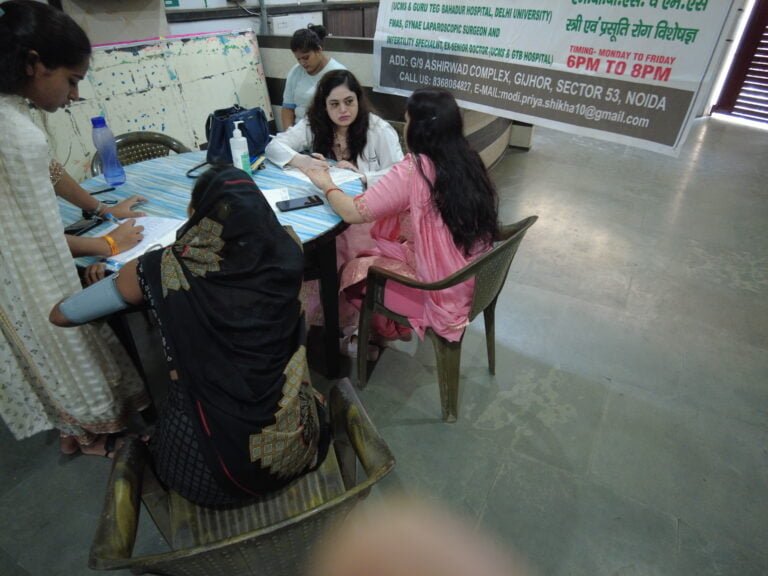







Community Service: Free Medical Camp by Modilifeline Women’s Clinic
This is an initiative by Modilifeline Women’s clinic and Dr. Priya Shika Modi.
Modilifeline women’s Clinic organizes a free medical camp to increase awareness among the public about women’s health. Dr. Priya Shikha Modi, a renowned gynecologist and obstetrician, founded the clinic with the vision of empowering women through health education and awareness. Dr. Modi believes that women’s health is not only a medical issue but also a social and economic one, as it affects the well-being of families and communities.

By Dr. Priya Shikha Modi, MBBS, MS, DNB (gynecology and obstetrics), FMAS (Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery) What is abnormal...
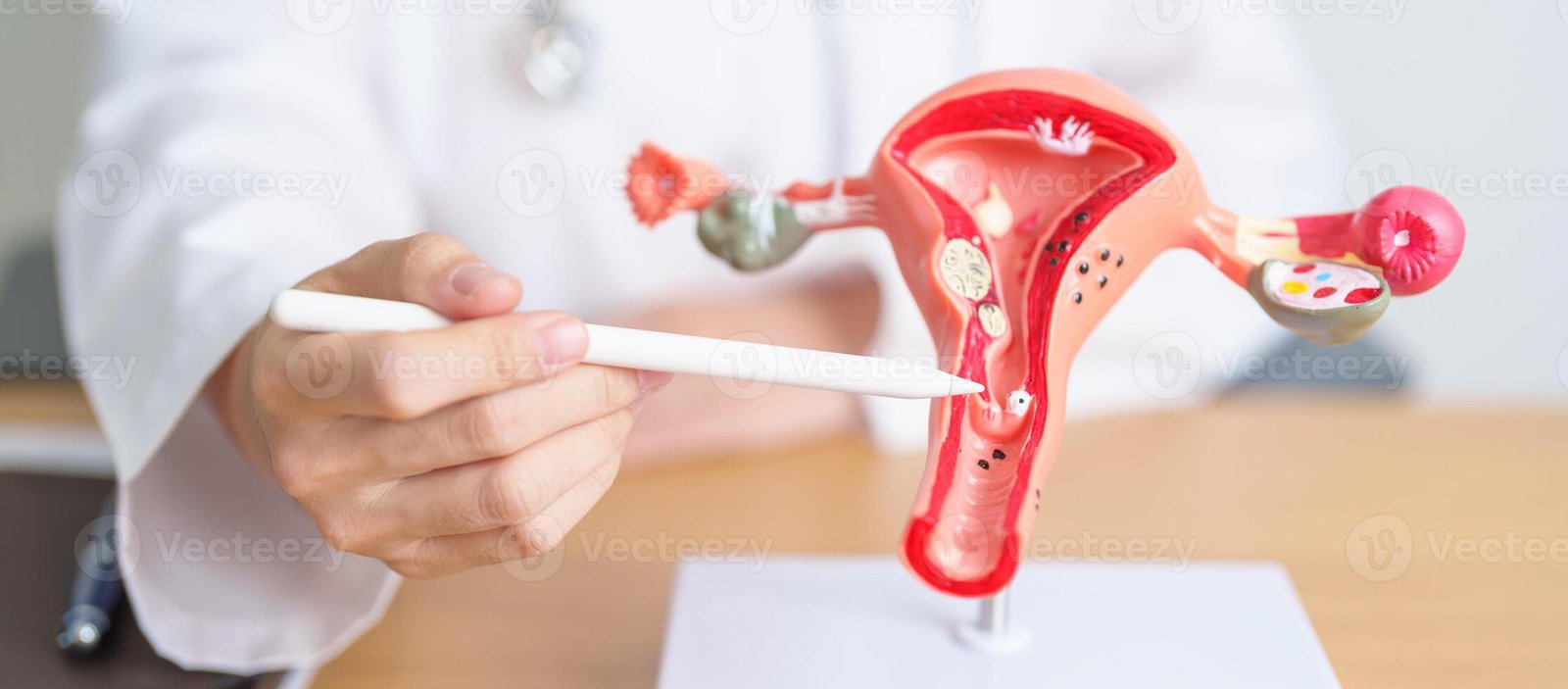
By Dr. Priya Shikha Modi, MBBS, MS, DNB (gynecology and obstetrics), FMAS (Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery) What is PCOS?...
By Dr. Priya Shikha Modi, MBBS, MS, DNB (gynecology and obstetrics), FMAS (Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery) What are ovarian...

By Dr. Priya Shikha Modi, MBBS, MS, DNB (gynecology and obstetrics), FMAS (Fellowship in Minimal Access Surgery) What are uterine...
You can make an appointment by calling the phone number 91-8368084837/91-9310282567, or you can WhatsApp in the same number by stating your name.
Yes, it is important to book an appointment, as it decreases your waiting time.
If you come without an appointment, it may be that you need to wait longer than usual.
More than 90% of women who have this surgery with us go home in under 24 hours. Women with TLH have less blood loss during surgery, need fewer pain-relieving medicines, recover quickly from surgery, and have fewer post-operative adhesions.
No. Not all cysts in the ovaries need surgical removal. The decision is based on the patient’s history and symptoms, as well as the results of imaging studies such as an ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan.
A laparoscopic approach can successfully remove most cysts. However, we may offer an open surgery if we deem it safe, taking into account your medical history and investigations. There will be occasions where open surgery may be offered, especially for those with any suspicion of ovarian cancer.
This is a condition in which a pregnancy is implanted outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube.
Not all ectopic pregnancies need surgical treatment. Based on your symptoms, ultrasound scan findings, and a particular blood test, your doctor may be able to avoid surgery.
No. Depending on certain factors, it is possible to conserve the tube. However, the main risk of this procedure is persistent trophoblast (incomplete pregnancy removal), which may necessitate further treatment in the form of either an injection (Methotrexate) or further laparoscopy at a later date to remove the affected tube.
Join our Facebook community for educational and informative videos on women's health by our renowned gynecologist Dr. Priya Shikha Modi. By joining our group, You will also be part of a supportive community of women who share their experiences and learn from each other & get heard.
By subscribing to Dr. Priya Shikha Modi's channel, you will get access to exclusive live sessions, Q&A educational, and informative videos on women’s health. We update videos regularly on our YouTube channel and live sessions for more & uplifting tips for better women's health. Make sure to subscribe to our channel.
Connect with Dr. Priya Shikha Modi & get tips on women's health, Via our Instagram handle, Get daily posts, stories, reels & more on topics like menstrual hygiene, fertility, pregnancy, menopause & more. One can interact live with Dr. Priya & share their views & experiences. Join our community that empowers healthy women.
Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Best doctor in noidaPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I had visited with my wife during her pregnancy. Dr Priya is highly skilled and experienced doctor also available after the clinic on calls and chats regularly She is very polite and familiar doctor.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Dr priya shikha modi one of the best doctor in noida. She is very genius doctor. Updated knowledge. Friendly behavior. Never misguide to pateint. Communication also good. Must visit at clinic.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Excellent performance, good treatment and excellent work ..Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. One of the Best Gynic clinic in noida . Dr priya Shikha takes care of her patients very well . Treatment is effective & good . I highly recommend itPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Great doctor with finest skills.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very nice behavior, best gynecologist.